ANALYSIS OF SOLARWINDS HACK
WHAT IS SOLARWINDS HACK?
SolarWinds Hack is a cyberattack discovered recently in the Unites States. It was mainly targeted against US Government and agencies and may have affected several other companies across the world. It was first reported in Dec 8, 2020; when a prominent cyber security company FireEye confirmed an attack on their systems, through a blog. The methods used by the attackers were novel and they tried to steel information related to certain government customers.
MODUS OPERANDI
Attackers used a different mode of operation (Supply Chain Attack) in this case.
SolarWinds is an IT company which supplies IT management software called Orion to several Government and other private organizations. As per published client lists, Orion business software has been used by more than 33,000 companies, which includes 400+ Fortune 500 companies and 10+ telecom operators in US.
In a Supply Chain attack, instead of directly attacking the government or a private organization’s network, attackers target a third-party vendor who supplies software to these entities (which in this instance is Orion software from SolarWinds).
How did they gain access?
Hackers gained access to victim’s systems via Trojanized software updates to Orion .Software updates were exploited to install the Sunburst malware into servers running with Orion. Adversaries used Orion software updates that company distributed between March and June 2020 to plant the malicious code in the target’s servers. Once installed, this malware provides a backdoor entry for hackers to enter the systems and networks to steal data. This malware is capable of gathering critical information, running remote commands, and exfiltrating the results to an attacker-controlled server stealthily. After systems were compromised, “lateral movement and data theft” did also take place. It was estimated that infected software updates were installed by more than 18,000 customers.
Organizations are advised to check whether they have installed the vulnerable versions of 2019.4 HF 5 through 2020.2.1, released between March 2020 and June 2020 on their servers.
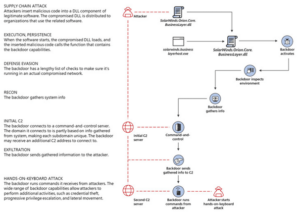
Source: The hacker news, Dec 22 2020
According to FireEye, attackers used multiple techniques to avoid being detected by various scanners. Virus activities were blended with legitimate Orion business activities in such a way that they looked genuine and normal.
Impact of SolarWinds hack!
SolarWinds says 18,000 of their clients have been impacted. A New York Times report said parts of the Pentagon, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the State Department, the Justice Department, and others, were all impacted. It is considered to be one of the biggest ever cyberattack targeted against US Government and Agencies. According to FireEye, it is likely that the issue began in March 2020 and has been ongoing for months.
Evidence suggest that attackers have been conducting dry runs as early as October 2019. The compromised DLL file is digitally signed implies a compromise of the company’s software development or distribution pipeline.
The extent of data stolen or compromised is still unknown, given the scale of the attack is still being discovered. The sheer scale of the cyber-attack remains unknown even today. Though the specific number of infected victims remains unknown at this time, it has steadily increased since cybersecurity firm FireEye revealed it.
How difficult was to detect it?
Attackers managed to modify a plugin that was distributed as part of Orion platform updates. The Trojanized component was digitally signed, which contained a backdoor that communicates with third-party servers controlled by the attackers.
- The malware masquerades its network traffic as the Orion Improvement Program (OIP) protocol and stores reconnaissance results within legitimate plugin configuration files allowing it to blend in with legitimate SolarWinds activity.
- The backdoor uses multiple obfuscated blocklists to identify forensic and anti-virus tools running as processes, services, and drivers.
- The attackers kept their malware footprint very low, preferring to steal and use credentials to perform lateral movement through the network and establish legitimate remote access.
- The backdoor was used to deliver a lightweight malware dropper that has never been seen before and which FireEye has dubbed TEARDROP. This dropper loads directly in memory and does not leave traces on the disk.
- To avoid detection, attackers used temporary file replacement techniques to remotely execute their tools. This means they modified a legitimate utility on the targeted system with their malicious one, executed it, and then replaced it back with the legitimate one.
- A similar technique was used in the temporary modification of system scheduled tasks by updating a legitimate task to execute a malicious tool and then reverting the task back to its original configuration.
- This is some of the best operational security exhibited by a threat actor that FireEye has ever observed, being focused on detection evasion and leveraging existing trust relationships.(Source: CSO Online, Dec 15 2020).
How to protect your VMWare vSphere?
SolarWinds Orion hack is VMWare vSphere vulnerable. In order to ensure that your VMWare ESXi hosts are protected, SolarWinds Orion updates, affected by the malware are installed, take the following precautionary actions:
take the following precautionary actions:
- Change ESXi root passwords
- Remove Active Directory Access from VMware vSphere
- Control who has access to your VMware vSphere management network
- Monitor logins and other activities in your VMware vSphere environment (For what?)
- Upgrade the software to 2020.2.4
More similar malware attacks?
Microsoft confirmed that it had found evidence of this malware (SolarWinds Hack) on some of their systems, and already issued warning to their customers.
Further investigation of the SolarWinds compromise by Microsoft 365 research team has also lead to the discovery of additional malware (dubbed as Supernova) that affects the SolarWinds Orion software, which is likely to be by a different threat actor. Digital forensic evidence showed the possibility of such a different threat actor abusing the Orion software to drop a similar backdoor on target systems.
Researchers from Palo Alto Networks said the Supernova malware is compiled and executed in-memory, permitting the attacker to bypass endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems and “deploy full-featured – and presumably sophisticated – .NET programs in reconnaissance, lateral movement and other attack phases.”
FURTHER ALERTS & REPORTS
- The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), in an alert last week, said it found evidence of initial infection vectors using flaws other than the SolarWinds software. CISA took the unusual step of issuing an emergency directive ordering all federal agencies to immediately disconnect the affected Orion products from their networks.
- Cybersecurity firms Kaspersky and Symantec have said they each identified 100 customers who downloaded the Trojanized package containing the Sunburst backdoor, with the latter finding traces of a second-stage payload called Teardrop in a small number of organizations.
- So far, several US government agencies and private companies, including Microsoft, Cisco, Equifax, General Electric, Intel, NVIDIA, Deloitte, and VMware have reported finding the malware on its servers.
- Cisco said: “We have isolated and removed Orion installations from a small number of lab environments and employee endpoints. At this time, there is no known impact to Cisco products, services, or to any customer data. We continue to investigate all aspects of this evolving situation with the highest priority.”
- FireEye reported that the threat actor had stolen its arsenal of Red Team penetration testing tools, making it so far the only instance where the attackers escalated access thus far. FireEye has suffered an intrusion that resulted in the theft of some 300 proprietary software tools the company provides to clients to help secure their IT operations.
- 14, Microsoft took control over a key domain name — avsvmcloud.com — that was used by the SolarWinds hackers to communicate with systems compromised by the backdoored Orion product updates.
- Alan Paller, director of research for the SANS Institute, a security education and training company based in Maryland, said the attackers likely chose to prioritize their targets based on some calculation of risk versus reward.
- SolarWinds’ has incurred financial and reputational damage since news of the breach first broke .
- No other governments have announced compromises of their systems yet.
SUMMARY
SolarWinds hack is considered to be one of the biggest ever cyberattack targeted against US Government and Agencies. The methods used by the attackers were a novel supply chain attack. The extent of data stolen or compromised remains unknown even today. But it has steadily increased since cybersecurity firm FireEye revealed it. Software supply chain attacks are some of the hardest type of threats to prevent or detect.
Interested in reading similar articles? Please follow us on LinkedIn.
About The Author

Dr. Anil Kumar
VP Engineering
Founder | Vice President | CTO | Architect | Consultant | Mentor | Advisor | Faculty
Solution Architect & IT Consultant with more than 25 yrs of IT Experience. Served various roles with both national and international institutions. Expertise in working with both legacy and advanced technology stacks in various business domains.

